Background
A vast majority of finished AGV/AMRs were streamed into either manufacturing or warehouse logistics. Higher social acceptance and more sophisticated robotic crafts enabled mobile robots to offer services in more settings, like security patrol, road sweeping, construction sites, courier services, to mention but a few.

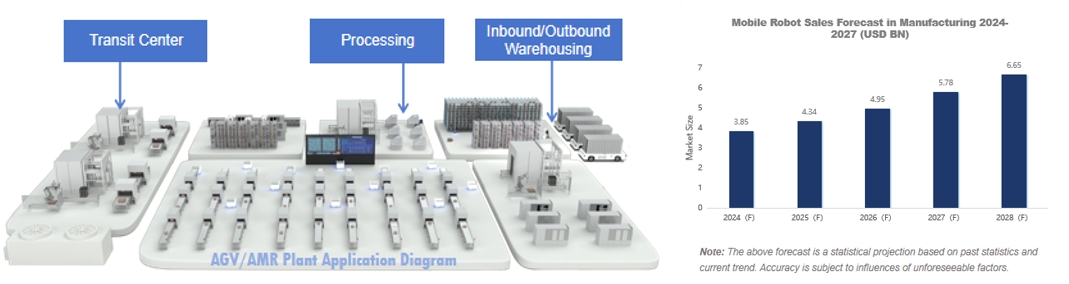
AGV/AMR earned USD 3.4 billion from manufacturers
In manufacturing plants, AGV/AMRs were primarily employed in materials transport, assembly line, and automated warehouse management, effectively boosting operational efficiency of factories and helping cut labor costs.
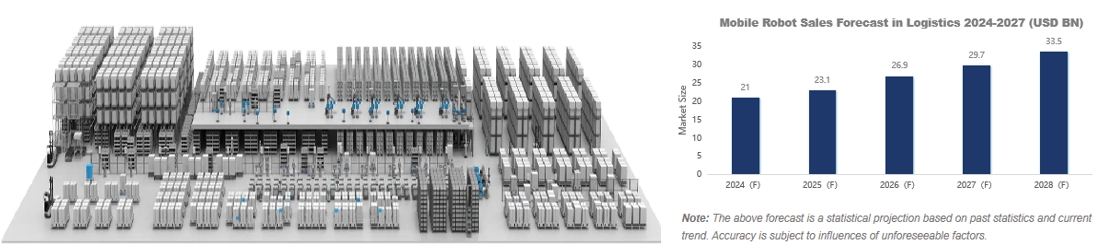
Warehouse AGV/AMRs sales were valued at USD 1.85 Bn.
Several types of AGV/AMRs were more common than others in warehouses. Apart from Kiva-type robots and forklifts, a diverse array of AGV/AMR fleet had assumed such roles as tote-bearing, shuttle transport, packing and picking. Meanwhile, there was a tendency for a transition to combined formula, such as Kiva + tote robots, shuttle cart + AGV/AMR, etc.
Beyond the boundary
Technological innovations are extending the extent mobile robotics could possibly reach. AGV/AMR fleets had infiltrated into more aspects of our work and life, mingling closer with modern city life.